Robots Coaching Humans
Leveraging expert coach corrections to create a "robot coach"
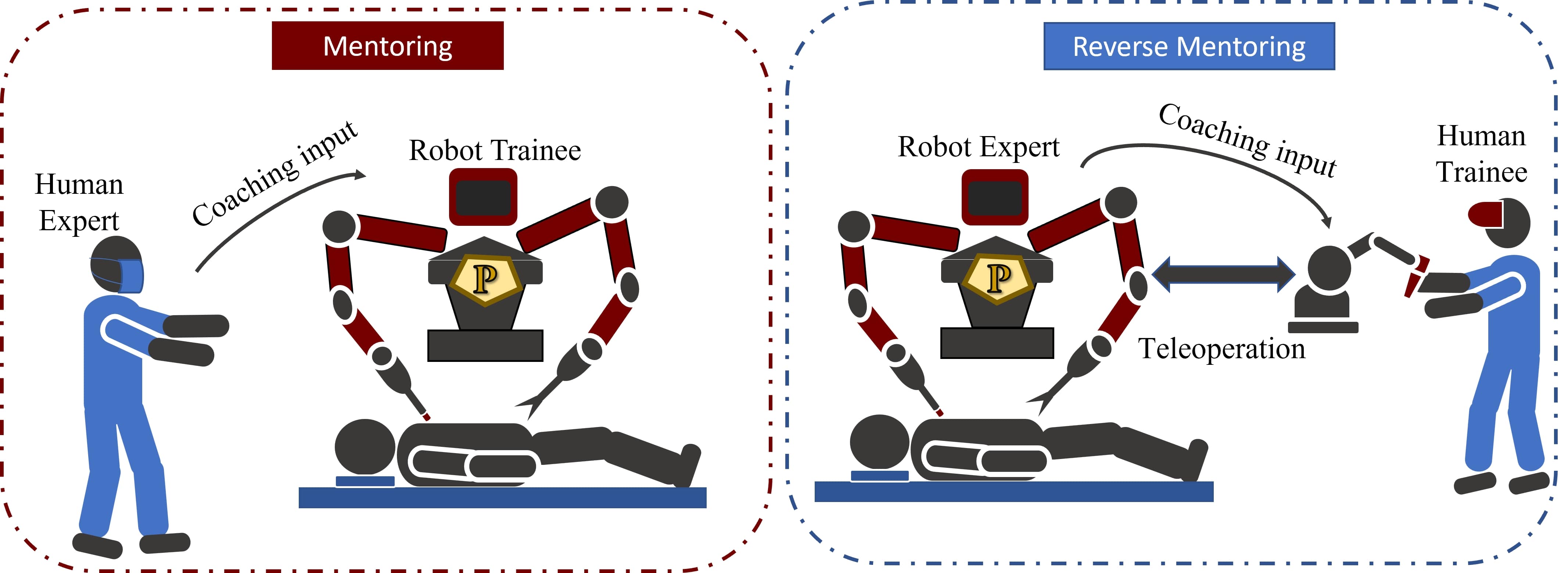
A robot gains task expertise throug learning from demonstrations and coaching using CbD. The robot expert can now improve collaborative task performance by playing a more active role by either requesting or providing feedback to the human collaborator. The knowledge from coaching enables the robot to have richer set of interactions, with interchangeable roles, where robot is not only a learner but can be a teacher to the human collaborator.
Bi-directional coaching is a relatively unexplored domain which is gaining interest recently.However, similar to human tutelage, the feedback provided by the robot should be adapted to the style of the collaborator.
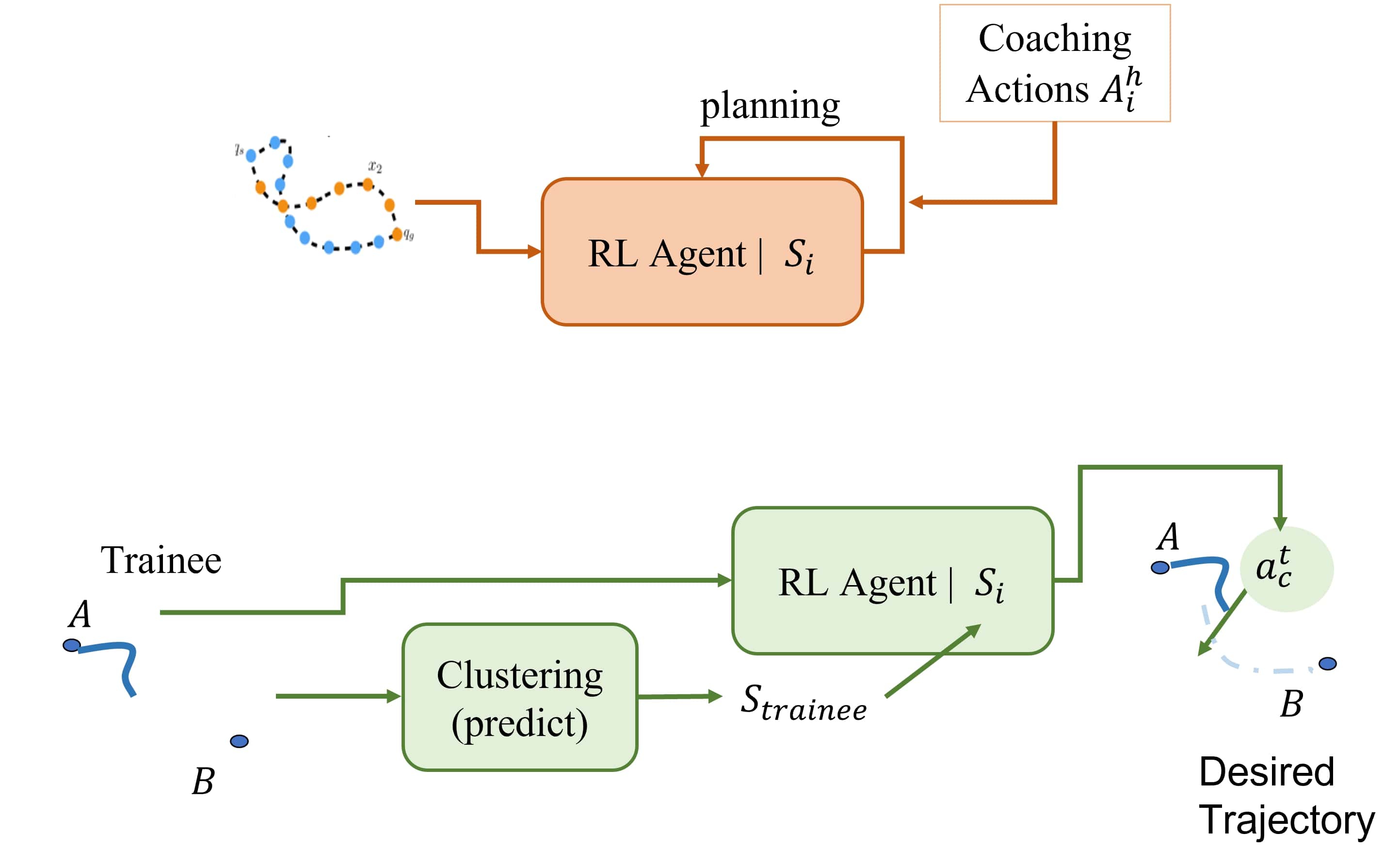
To create a robot coach that provides style-guided feedback, a two-stage learning process is developed - learning the styles and learning to mentor. The system is designed as a hierarchical learning problem with base agent learning to represent styles and higher-level mentoring policy which provides feedback based on the trainee’s performance and style.
The task null-space trajectories are grouped using an unsupervised clustering method to generate the style clusters and identify their mean and variance. For learning to mentor, the robot learns a policy through off-policy deep reinforcement learner per given style, trained to estimate mentoring corrections based on the current trajectory of trainee and estimate of his performance. The agent is trained on the set of corrective actions human experts provided during the robot training.
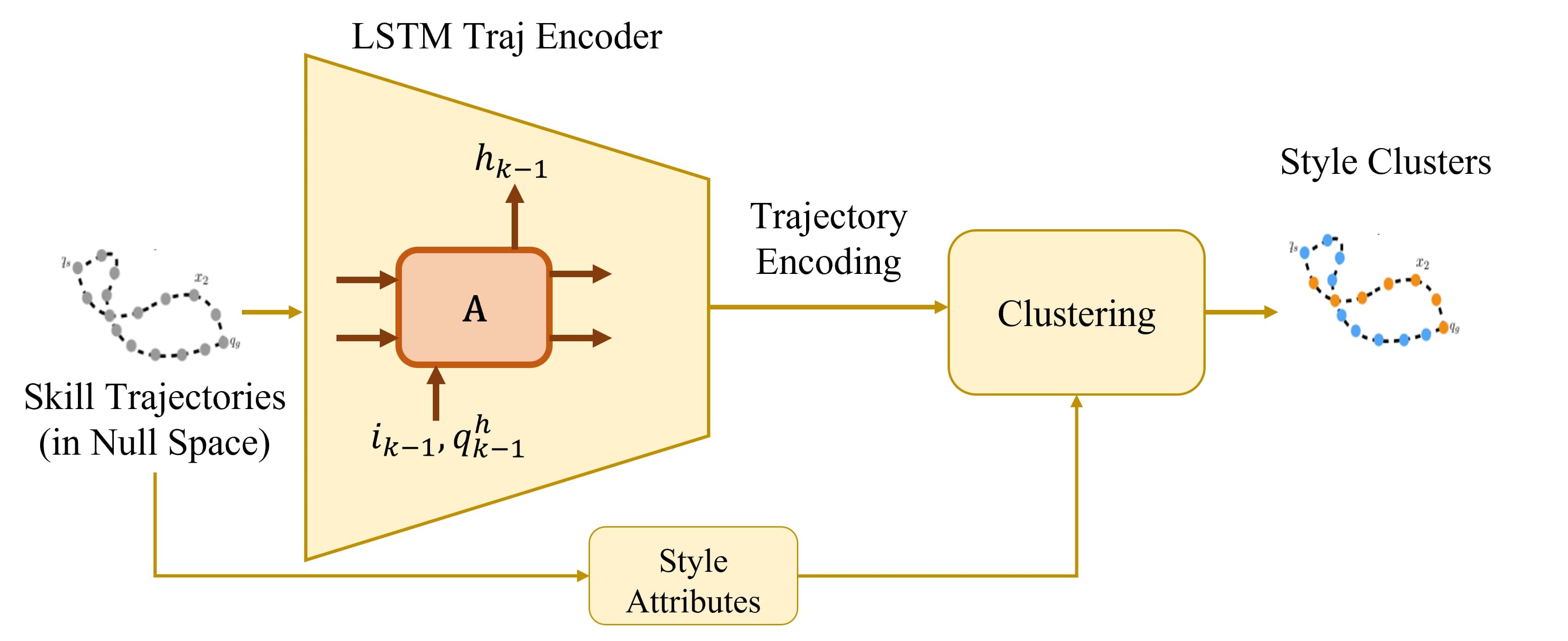
When a novice human is performing the task, the robot agent estimates the distance of the current trajectory to each of the style clusters using dynamic time warping. The human trajectory’s style is then classified based on the statistics of the style clusters. The proposed policy for the robot mentor generates corrective actions, if necessary, to improve the human’s performance. The proposed framework for bi-directional mentoring enables semi-autonomous execution of medical procedures using a robotic system. Further, the framework provides a system for improving training of novice medical personnel using a trained robot by leveraging the expertise of both humans and robots.